SELF JOIN
Contents
import sqlalchemy
engine = sqlalchemy.create_engine('postgresql://bob:1234@localhost:5432/dvdrental')
engine.execution_options(isolation_level="AUTOCOMMIT")
%load_ext sql
%sql $engine.url
'Connected: bob@dvdrental'
SELF JOIN#
There may be a situation where we may want to combine rows in a table with other rows in the same table, by using a join statement. To join a table to itself, we must use a table alias in order to tell apart the left table from the right table (they’re both the same table).
Example: Comparing rows in the same table#
Let’s say we want to compare those customers whose first names are equal to other customers last names:
%%sql
SELECT
a.customer_id, a.first_name, a.last_name, b.customer_id, b.first_name, b.last_name
FROM customer AS a
JOIN customer AS b
ON a.first_name = b.last_name
LIMIT 10;
* postgresql://bob:***@localhost:5432/dvdrental
10 rows affected.
| customer_id | first_name | last_name | customer_id_1 | first_name_1 | last_name_1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 | Rose | Howard | 157 | Darlene | Rose |
| 67 | Kelly | Torres | 74 | Denise | Kelly |
| 118 | Kim | Cruz | 233 | Lillie | Kim |
| 230 | Joy | George | 307 | Joseph | Joy |
| 253 | Terry | Carlson | 265 | Jennie | Terry |
| 299 | James | Gannon | 71 | Kathy | James |
| 301 | Robert | Baughman | 331 | Eric | Robert |
| 308 | Thomas | Grigsby | 12 | Nancy | Thomas |
| 312 | Mark | Rinehart | 336 | Joshua | Mark |
| 314 | George | Linton | 230 | Joy | George |
Instead of using the JOIN statment explicitely, we could write the query above as follows;
%%sql
SELECT
a.customer_id, a.first_name, a.last_name, b.customer_id, b.first_name, b.last_name
FROM customer AS a, customer AS b
WHERE a.first_name = b.last_name
LIMIT 10;
* postgresql://bob:***@localhost:5432/dvdrental
10 rows affected.
| customer_id | first_name | last_name | customer_id_1 | first_name_1 | last_name_1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 | Rose | Howard | 157 | Darlene | Rose |
| 67 | Kelly | Torres | 74 | Denise | Kelly |
| 118 | Kim | Cruz | 233 | Lillie | Kim |
| 230 | Joy | George | 307 | Joseph | Joy |
| 253 | Terry | Carlson | 265 | Jennie | Terry |
| 299 | James | Gannon | 71 | Kathy | James |
| 301 | Robert | Baughman | 331 | Eric | Robert |
| 308 | Thomas | Grigsby | 12 | Nancy | Thomas |
| 312 | Mark | Rinehart | 336 | Joshua | Mark |
| 314 | George | Linton | 230 | Joy | George |
In the query above we specify the same table twice, separated by a comma (instead of a JOIN) and aliased to a and b. For this reason, instead of using ON to provide the condition, we do it using a WHERE clause.
Example 2: Querying Hyerarchical data using a Self Join#
A common SQL code interview example is the one where we’re presented with a single employee table, which employees and managers (they all are employees, but some manage others). Check the following diagram for clarification:
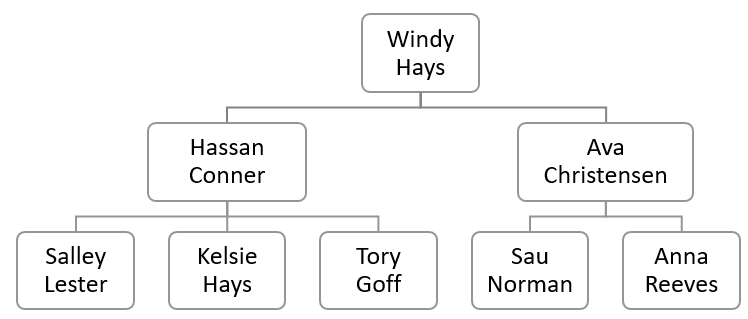
The table containing the employees above would be:
id |
first_name |
last_name |
manager_id |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Windy |
Hays |
NULL |
2 |
Ava |
Christensen |
1 |
3 |
Hassan |
Conner |
1 |
4 |
Anna |
Reeves |
2 |
5 |
Sau |
Norman |
2 |
6 |
Kelsie |
Hays |
3 |
7 |
Tory |
Goff |
3 |
8 |
Salley |
Lester |
3 |
As you can see, the Windy Hays row shows a manager_id with the value NULL, because she’s the top dog 🐶.
Creating a New Database and Table#
Let’s create a new database (let’s call it acme) for demonstrating this query:
createdb -h localhost -p 5432 -U bob acme
Then we have to create a connection to it:
import sqlalchemy
engine = sqlalchemy.create_engine('postgresql://bob:1234@localhost:5432/acme')
engine.execution_options(isolation_level="AUTOCOMMIT")
%load_ext sql
%sql $engine.url
The sql extension is already loaded. To reload it, use:
%reload_ext sql
'Connected: bob@acme'
Now let’s create the employee table, and insert some rows in it:
%%sql
CREATE TABLE employee (
employee_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
manager_id INT
);
INSERT INTO employee (
employee_id,
first_name,
last_name,
manager_id
)
VALUES
(1, 'Windy', 'Hays', NULL),
(2, 'Ava', 'Christensen', 1),
(3, 'Hassan', 'Conner', 1),
(4, 'Anna', 'Reeves', 2),
(5, 'Sau', 'Norman', 2),
(6, 'Kelsie', 'Hays', 3),
(7, 'Tory', 'Goff', 3),
(8, 'Salley', 'Lester', 3);
* postgresql://bob:***@localhost:5432/acme
postgresql://bob:***@localhost:5432/dvdrental
(psycopg2.errors.DuplicateTable) relation "employee" already exists
[SQL: CREATE TABLE employee (
employee_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
manager_id INT
);]
(Background on this error at: https://sqlalche.me/e/14/f405)
Let’s say we want to pull data which contains:
Employee full name
Full name of his/her manager
%%sql
SELECT
e.first_name || ' ' || e.last_name AS employee,
m.first_name || ' ' || m.last_name AS manager
FROM
employee e
JOIN employee m ON m.employee_id = e.manager_id
ORDER BY manager;
* postgresql://bob:***@localhost:5432/acme
postgresql://bob:***@localhost:5432/dvdrental
7 rows affected.
| employee | manager |
|---|---|
| Sau Norman | Ava Christensen |
| Anna Reeves | Ava Christensen |
| Salley Lester | Hassan Conner |
| Kelsie Hays | Hassan Conner |
| Tory Goff | Hassan Conner |
| Ava Christensen | Windy Hays |
| Hassan Conner | Windy Hays |
As you can see, the employee column doesn’t contain the name of the head honcho, Windy Hays.

