So you’ve been hearing about a lot of good things about Deno, want to try it out but don’t know where to start? Don’t worry, got you covered son! How about we set up a React project using the Jurassic runtime and Vite.js? This guide will also show you how to install Deno.
NOTE
Deno is a simple, modern, and secure runtime for JavaScript and TypeScript that uses V8 and is built in Rust. It’s a great alternative to Node.js, and promises to be more secure and faster.
Installing Deno
The Deno installation in macOS/Linux, is very simple, you just need to run the following command:
curl -fsSL https://deno.land/install.sh | shTIP
In macOS, you can also install Deno using Homebrew, just run brew install deno. Or using your package manager in Linux.
For Windows, you can use PowerShell:
irm https://deno.land/install.ps1 | iexWARNING
For the time you’re reading this, the installation process may have changed. Please refer to the official Deno installation guide for the most up-to-date instructions.
Starting a new React project
To start a new React project using Deno, we’ll use Vite.js, a build tool that aims to provide a faster and leaner development experience for modern web projects. To create a new React project, run the following command:
deno run -RWE npm:create-vite-extra@latestThe npm: prefix is used to indicate that the create-vite-extra script (that will help you create a new Vite project with extra templates and options) should be fetched from the npm registry. This allows Deno to run npm packages directly without needing a separate package manager like npm or yarn.
NOTE
The -RWE flags in the deno run command are used to grant specific permissions to the script being executed. Here’s what each flag stands for:
-R(short for--allow-read) grants the script permission to read files and directories.-W(short for--allow-write) grants the script permission to write to files and directories.-E(short for--allow-env) grants the script permission to access environment variables.
Remember when we mentioned that Deno is more secure? This is one example.
This command will start a prompt asking you for the project name, template, and other options. Choose the React template and follow the instructions. When it finishes, you’ll see the following message:
Scaffolding project in /home/bob/react-deno...
Done. Now run:
cd react-deno deno task devThat’s it, not much to be done. Just go to the project folder and run deno task dev to start the development server. You can now start coding your new React project using Deno!
Installing packages
In the previous section we’ve seen how to create a new React project using Vite.js. Now, let’s see how to install new packages in your project. For example, let’s install React Router, a popular routing library for React:
deno add npm:react-router@latestTIP
Read our other post about React Router 7 to learn more about how to use it.
Formatting Code
Deno includes a built-in code formatter called deno fmt that can be used to format your code. To format all the files in your project, run the following command:
deno fmtBut running a command each time you want to format your code can be cumbersome. To make it easier, we’ll make it so that when we use a shortcut, our code is automatically formatted (it can be also be configured on save).
Installing the Deno VSCode Extension
We just have to open the Extensions panel in VSCode, and search for the Deno extension.
Initialize Workspace Configuration
Once the Deno extension has been installed, you can initialize the workspace configuration by running the Deno: Init command from the command palette (Cmd+Shift+P on macOS, Ctrl+Shift+P on Windows/Linux).
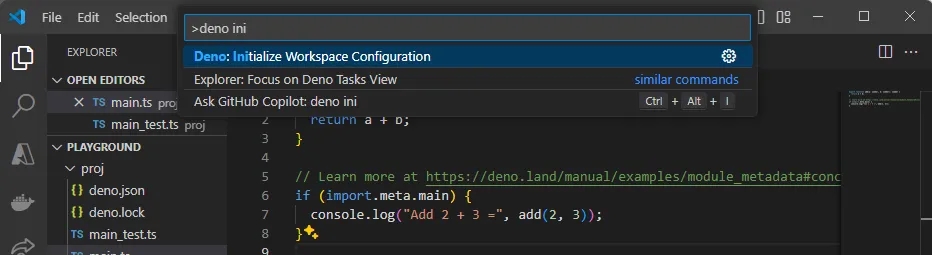
A file called .vscode/settings.json will be created in your workspace with the following configuration:
{ "deno.enable": true,}That enables Deno in your workspace. Now, to configure the code formatting, we can add the following to the file above:
"[typescript]": { "editor.defaultFormatter": "denoland.vscode-deno"},"[javascript]": { "editor.defaultFormatter": "denoland.vscode-deno"}TIP
Optionally, if you want to format the code on save, add the following:
"editor.formatOnSave": trueAlso, we can configure the formatting style in the deno.json file:
"fmt": { "options": { "useTabs": false, "lineWidth": 80, "indentWidth": 2, "singleQuote": true, "proseWrap": "always", "semiColons": false } }WARNING
Be careful with the formatting settings, if you are used to the ones used by Prettier, you may have to adjust them; e.g. "semi": false doesn’t work in Deno.